We use the lens equation
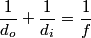 where 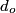 is the distance from the object to the lens, is the distance from the object to the lens, 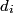 is the distance from the image to the lens, and is the distance from the image to the lens, and 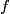 is focal length. This equation can be used with two lenses by first applying it to find the first lens, ignoring the second lens, and then applying it to the second lens, ignoring the first lens, and taking the image of the first lens as the object of the second lens. is focal length. This equation can be used with two lenses by first applying it to find the first lens, ignoring the second lens, and then applying it to the second lens, ignoring the first lens, and taking the image of the first lens as the object of the second lens.The conventions for the lens equation tell us that the focal length is positive for a converging lens and negative for a diverging lens. Since both of the lenses in this problem are converging, the focal lengths are 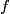 are are 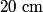 and and 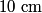 , respectively. The object distance for the first lens is positive, because the object is on the same side of the lens from which the light is coming. Thus, the lens equation for the first lens is: , respectively. The object distance for the first lens is positive, because the object is on the same side of the lens from which the light is coming. Thus, the lens equation for the first lens is: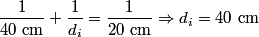 This is 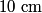 behind the second lens. Therefore, behind the second lens. Therefore, 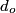 in the lens equation for the second lens is in the lens equation for the second lens is 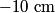 . Thus, the lens equation for the second lens is . Thus, the lens equation for the second lens is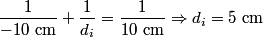 The image distance is positive when the image is on the opposite side of the lens from which light is coming. Therefore, the image is 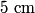 to the right of the second lens. Therefore, answer (A) is correct. to the right of the second lens. Therefore, answer (A) is correct. |